What Is an Emergency Braking System in Vehicles?
In this article we read
ToggleIn this article, we will thoroughly explore the emergency braking system in vehicles. As you may know, automakers have continuously aimed to improve vehicle quality since the beginning of car manufacturing. These advancements are evident in every aspect—design, engine performance, suspension and stability systems, and especially in safety and braking systems.
Undoubtedly, safety is one of the most critical pillars of a vehicle, and any improvement in this area plays a fundamental role in the overall quality of the car. Reputable manufacturers have always taken pride in their vehicles’ safety features, often highlighting them in product presentations and advertisements.
Over the past two decades, significant technological advancements—including the introduction of sensors and high-resolution cameras—have led to the widespread adoption of active safety systems in vehicles. These systems rely heavily on sensor-based technologies and have dramatically enhanced vehicle safety.
One major outcome of these developments is the creation of the Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) system. This innovation represents a major step forward in braking technology and vehicle safety.
Stay with Mana Tormoz…
From ABS to Automatic Emergency Braking
One of the earliest major advancements in vehicle braking systems was the introduction of the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). This system allows drivers to make full use of their brakes without the risk of wheel lock-up. ABS not only enhances safety but also works in conjunction with Electronic Stability Control (ESP) to provide optimal performance in challenging conditions such as slippery roads or high-speed cornering.
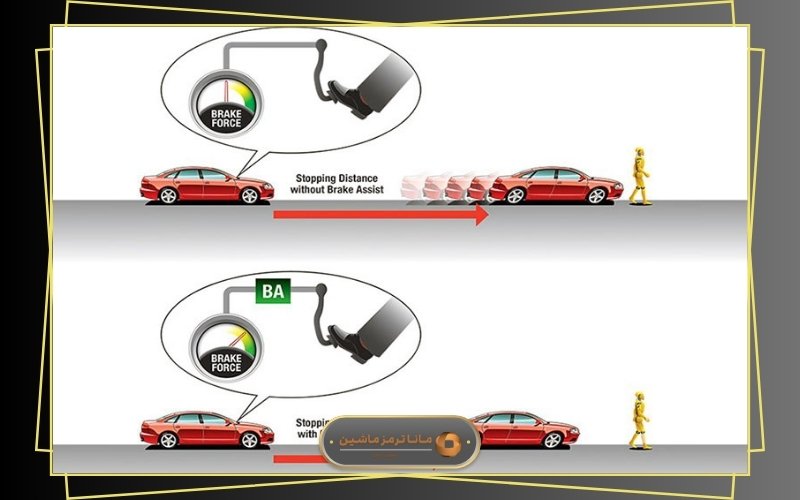
Although ABS and ESP perform well, they still require direct input from the driver. In other words, if the driver takes no action, these systems remain inactive. For this reason, automakers introduced the Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) system. Also known as Brake Assist or Brake Support, AEB shares the same purpose: to automatically activate the brakes in critical moments and reduce the vehicle’s speed.
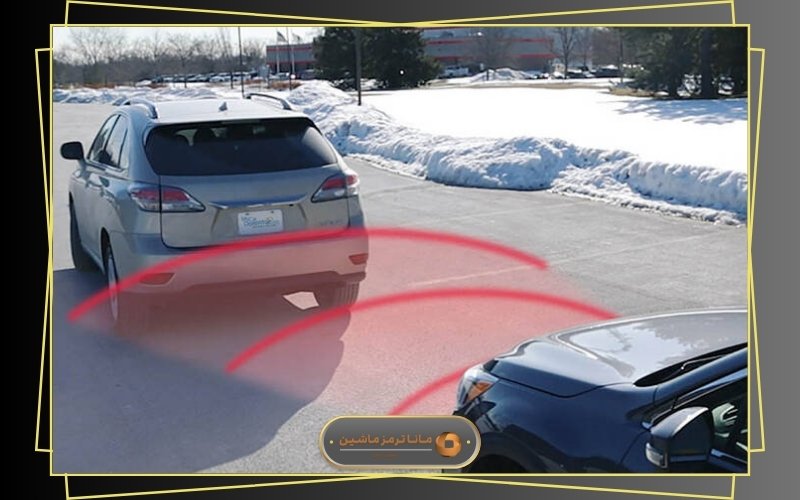
To better understand how the AEB system works, imagine a scenario where the system detects that you are not braking in time. It intervenes and applies the brakes on your behalf. This function is generally active at speeds up to about 60 km/h and is specifically designed to prevent collisions with obstacles ahead.
The effectiveness of this system is especially significant in front-end and rear-end collisions. According to statistics, these types of crashes account for nearly 80% of all accidents and often result in substantial financial damage.
How Does the Vehicle Emergency Braking System Work?
Modern vehicles today are equipped with advanced diagnostic systems that use radar and laser technology to accurately measure the distance between vehicles. These technologies have directly enabled features such as adaptive cruise control. These systems can detect the distance from other vehicles and automatically adjust the vehicle’s speed to match the traffic ahead—without driver input. In other words, adaptive cruise control adjusts itself automatically and does not require manual activation or deactivation.
One of the most significant innovations in this field was the introduction of the Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) system, first launched by Volvo in 2009. This system uses the same radar sensors to assess distances and automatically applies the brakes when it detects a dangerous reduction in the gap between vehicles to prevent a collision.
Different car manufacturers have implemented their own versions of AEB. For example, Subaru integrated AEB with its EyeSight system, which replaces radar with advanced cameras to analyze 3D images and evaluate distances.
How Does Emergency Braking Work?
The high processing speed of modern vehicle computers significantly increases driving safety. In critical situations, these computers can react much faster than a human driver and automatically activate the brakes. Thanks to the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), the system uses the maximum braking force to reduce speed and prevent collisions.
If the AEB system detects that the driver is already braking and the vehicle is on track to stop in time, it will not intervene, ensuring that driving remains smooth and uninterrupted. However, these systems are not flawless. In busy urban environments or heavy traffic, the system may become confused and engage the brakes repeatedly.
Still, the true value of AEB is revealed when it prevents a serious accident. Early versions of the system operated at speeds up to 30 km/h, but with recent advancements, they are now capable of functioning at speeds up to 60 km/h.
Radar and Camera Integration for Enhanced System Performance
Radars are highly effective in evaluating the position and movement of objects, but they are not as efficient as cameras when it comes to identifying the type of object. For this reason, modern AEB systems use a combination of radar and camera technologies. This integration allows the radar to accurately track the location and motion of objects, while the camera can distinguish between different types of obstacles such as vehicles, pedestrians, bicycles, and motorcycles. This hybrid approach significantly improves the performance and accuracy of the automatic emergency braking system.
The Importance of Including Emergency Braking Systems in All Vehicles
Renowned safety assessment organizations, such as ANCAP in Australia, strongly emphasize the need for all vehicles to be equipped with Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB). Just as systems like ABS, ESP, and traction control are mandatory in vehicles sold in the country, AEB is also expected to become a standard feature.
Although integrating advanced safety systems may raise manufacturing costs, this should not be a barrier to their inclusion. For instance, Volkswagen has equipped the base model of its city car, the Up, with AEB as standard—and the vehicle is available at a price of $13,990. This demonstrates that cost concerns should not prevent the implementation of critical safety technologies.
Availability of Emergency Braking Systems in Different Vehicles
However, some automakers follow a different approach. For example, while base models of the Volkswagen Tiguan come standard with AEB, other Volkswagen models require an additional payment to include this system. A similar pattern is seen in other brands as well. Companies like Skoda and Mazda offer these systems selectively in certain models. This strategy may indicate that automakers are aware of customer demand for safety features and aim to encourage buyers to opt for higher-priced models by including these features exclusively in premium trims.
The Need to Mandate Active Safety Systems by Law
Ultimately, the most effective way to ensure that advanced safety systems like AEB are included in all vehicles is to establish mandatory regulations for their implementation. Renowned safety organizations such as EURONCAP place special emphasis on active safety systems like Automatic Emergency Braking. Today, vehicles that lack such systems—even if they perform well in crash protection and occupant safety—may struggle to achieve the highest safety rating (5 stars).